Introduction
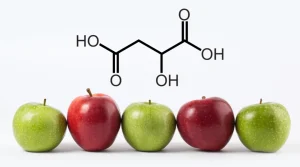
Malic acid, an organic compound with the formula C4H6O5, is a dicarboxylic acid found naturally in many fruits and vegetables. Recognized for its sour taste, malic acid is commonly used as a flavor enhancer in food products. It has two isomeric forms: L-malic acid, which is the naturally occurring form, and D-malic acid.
Malic acid plays a crucial role in several industries, such as food and beverages, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. Its ability to enhance flavor, preserve food, and act as an exfoliating agent in skincare products underscores its versatility. Additionally, it plays a role in energy production within the human body, making it valuable in the health and nutrition sectors.
Chemical Properties

Molecular Structure and Formula
Malic acid’s molecular structure comprises four carbon, six hydrogen, and five oxygen atoms (C4H6O5). The molecule features two carboxyl groups, which contribute to its acidic properties.
Physical Properties (Solubility, Melting Point, etc.)
Malic acid presents itself as a white crystalline powder. It is highly soluble in water, making it valuable for use in various aqueous solutions. The melting point of malic acid is approximately 130°C, with a specific gravity of 1.609.
Chemical Behavior and Reactions
Because it contains two carboxyl groups, malic acid can engage in a variety of chemical reactions, such as esterification and dehydration. These reactions make it useful in the synthesis of other compounds and industrial applications.
Sources of Malic Acid
Natural Sources (Fruits, Vegetables)
Malic acid is abundant in fruits such as apples, grapes, and cherries, contributing to their characteristic sour taste. Vegetables like tomatoes and carrots also contain malic acid, albeit in smaller amounts.
Synthetic Production Methods
In addition to natural sources, malic acid can be synthetically produced. One common method involves the hydration of maleic anhydride or fumaric acid. This synthetic production is essential for meeting the high demand in various industries.
Applications of Malic Acid
Food and Beverage Industry
Malic acid is widely utilized in the food and beverage industry as both a flavor enhancer and a preservative. It adds a tangy taste to candies, soft drinks, and bakery products, improving their overall flavor profile.
Cosmetic and Personal Care Products
In cosmetics, malic acid functions as an exfoliating agent. It helps in removing dead skin cells, promoting smoother and brighter skin. This characteristic makes it a favored ingredient in skincare products like facial cleansers and peels.
Pharmaceutical Uses
Malic acid is employed in the pharmaceutical industry due to its role in energy production and its inclusion in various medications. It is involved in the Krebs cycle, a key metabolic pathway in the human body, which highlights its importance in health and nutrition.
Agricultural Applications
In agriculture, malic acid improves soil quality and enhances plant growth. It functions as a soil conditioner and supplies essential nutrients that promote plant growth.
Health Benefits and Risks
Potential Health Benefits
Malic acid offers several health benefits. It aids in energy production, reduces muscle fatigue, and improves skin health. It is also incorporated into dental care products due to its ability to stimulate saliva production and reduce plaque formation.
Possible Side Effects and Risks
While malic acid offers many benefits, excessive consumption can result in gastrointestinal issues like stomach cramps and diarrhea. Therefore, it is crucial to consume malic acid in moderation to prevent potential side effects.
Environmental Impact
Biodegradability and Environmental Safety
Malic acid is biodegradable and considered environmentally safe. It presents minimal risk to ecosystems, making it a sustainable option for various applications.
Industrial Production’s Impact on the Environment
The industrial production of malic acid, however, can have environmental impacts. This includes emissions and waste generation. Ongoing efforts aim to develop more sustainable production methods to mitigate these environmental impacts.
Conclusion
Malic acid is a versatile compound with numerous applications in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. Its natural occurrence and synthetic production make it widely accessible and useful.
