Ascorbic Acid Manufacturer
We provide pure ascorbic acid powder with pharmaceutical grade and food grade, produced in facilities that comply with international standards such as BRC, GMP FSSC,IP, ensuring safety, reliability, and traceability. Advanced processes ensure stability, protect from oxidation, and guarantee longer shelf life.
We provide customized solutions to satisfy certain client needs, such as:
- Purity Levels: Food, medicine
- Powder Partical Sizes: 40-80 mesh and 100 mesh
- Packaging : 25 kg/carton or customized
- Formulations: Levels of solubility and combinations with additional substances.
By Source
Natural Dietary Sources
Ascorbic acid is naturally found in a variety of fruits and vegetables. Some of the richest natural sources include:
Fruits
- Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, limes, grapefruits)
- Berries (strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries)
- Kiwi
- Pineapple
- Mango
- Papaya
- Guava
Vegetables
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Kale
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Cauliflower
- Cabbage
- Potatoes (particularly new and sweet potatoes)
Other Plants
- Rose hips
- Acerola cherries
- Indian gooseberries (amla)
- Camu camu berries
Synthetic Sources
Synthetic ascorbic acid, chemically identical to natural sources, is widely used in dietary supplements and food fortification.
Supplements
- Vitamin C tablets, capsules, and chewables
- Vitamin C powders and crystals
- Effervescent Vitamin C tablets
- Liquid Vitamin C drops
Fortified Foods and Beverages
- Breakfast cereals
- Fruit juices
- Dairy products (such as certain types of milk and yogurt)
- Snack bars
FEATURED PRODUCTS


Ascorbic Acid
- Pharmaceutical Grade and Food Grade
- CAS:50-81-7
- Chemical Formula:C6H8O6
- Mesh:25 kg/carton or customized
- MOQ:1000 kg
- Delivery time:15~20days
- Start Port:QINGDAO,SHANGHAI
- Certification:BRC,GMP FSSC,IP
- Shelf life:3 years
By Form
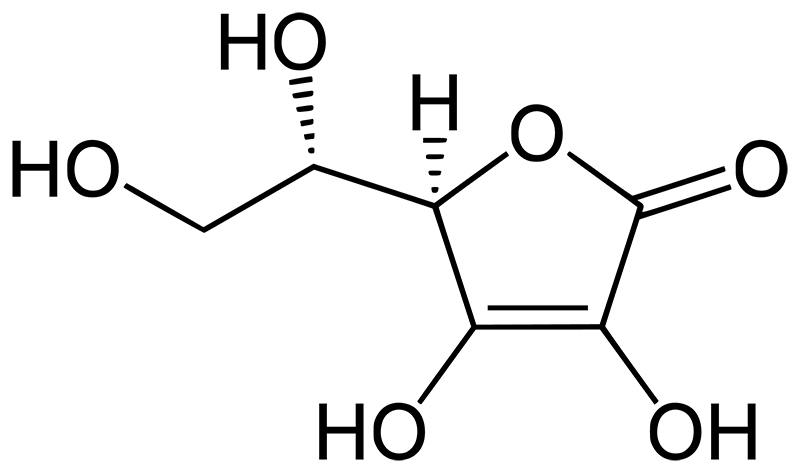
They fit within the stereoisomer category. The two types of ascorbic acid have different arrangements of their molecules around the chiral carbon atom.
L ascorbic acid
This is the naturally occurring form of Vitamin C and is biologically active in humans. It is the kind that is most frequently present in meals and dietary supplements.
D ascorbic acid
This is the mirror image of L-ascorbic acid and is not biologically active in humans. It is rarely found in nature and does not contribute to Vitamin C’s nutritional or therapeutic effects.
By Derivative
A derivative of ascorbic acid enhances stability and absorption while providing similar antioxidant and nutritional benefits as vitamin C.
Sodium Ascorbate
- Content: Sodium
- Feature: Provides both vitamin C and sodium. Useful for individuals who need to supplement sodium, but not recommended for those on a low-sodium diet.
Ferrous Ascorbate
- Content: Iron
- Feature: Combines vitamin C with iron, enhancing iron absorption. Beneficial for treating or preventing iron deficiency anemia.
Potassium Ascorbate
- Content: Potassium
- Feature: Supplies both vitamin C and potassium. Useful for individuals needing potassium supplementation, but must be used cautiously in those with kidney issues or potassium imbalances.
Calcium Ascorbate
- Content: Calcium
- Feature: Provides vitamin C along with calcium. Suitable for those who need additional calcium intake, such as individuals with osteoporosis or those at risk of calcium deficiency.
Magnesium Ascorbate
- Content: Magnesium
- Feature: Offers both vitamin C and magnesium. Beneficial for those who require magnesium supplementation, such as individuals with magnesium deficiency or those with muscle cramps.
By Fuction
Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being, with its antioxidant, collagen synthesis, immune-enhancing, iron absorption, neurotransmitter synthesis, and antiviral properties contributing to its numerous physiological functions. It serves several functions in the body:
Antioxidant Properties
Ascorbic acid acts as a powerful antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by reactive oxygen species. This contributes to reducing the risk of chronic ailments such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Collagen Synthesis
Ascorbic acid plays a vital role in synthesizing collagen, a structural protein abundant in skin, bones, cartilage, and connective tissues. Its significance extends to wound healing, tissue repair, and the preservation of skin and blood vessel integrity.
Immune Function
Ascorbic acid fortifies the immune system by bolstering the activity of key immune cells like lymphocytes and phagocytes. This augmentation of the body's defense mechanisms aids in combatting infections and potentially diminishes the intensity and duration of colds and respiratory illnesses.
Iron Absorption
Ascorbic acid facilitates the uptake of non-heme iron from plant-based sources by converting ferric iron into a more easily absorbable ferrous form. This aspect holds significant relevance for individuals adhering to vegetarian or vegan diets, where plant-derived iron sources typically exhibit lower absorption rates compared to those of animal origin.
Antiviral Properties
Ascorbic acid has been shown to exhibit antiviral properties, particularly against certain viruses such as the common cold virus (rhinovirus) and influenza virus. It has the potential to mitigate the intensity and duration of viral infections.
Neurotransmitter Synthesis
Ascorbic acid plays a role in synthesizing neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, essential for mood regulation, cognitive function, and overall brain health.
By Application
Ascorbic acid, a powerful antioxidant, enriches food nutrition, boosts skincare efficacy, and is vital in pharmaceuticals, showcasing extensive and diverse applications.
Food and Beverage Industry
Vitamin C finds widespread application as a food additive within the food and beverage sector. It serves multiple purposes, including:
- Antioxidant: Ascorbic acid helps to prevent oxidation and preserve the color, flavor, and nutritional value of food products.
- pH Regulator: It is used to adjust the acidity of food and beverage formulations to enhance taste and stability.
- Antimicrobial Agent: Ascorbic acid hampers microbial growth, thereby extending the shelf life of food products.
- Dough Conditioner: It enhances the texture and volume of baked goods by fortifying gluten and fostering yeast fermentation.
Nutritional Supplements
Ascorbic acid sees extensive use in crafting dietary supplements and fortified foods. It provides an easily absorbable form of vitamin C to help meet daily nutritional requirements and support overall health and immunity.

Food Preservation
Ascorbic acid serves as a natural preservative in food processing, prolonging the shelf life of perishable items like fruits, vegetables, and meat. It helps to inhibit enzymatic browning, microbial growth, and oxidation, thereby maintaining product quality and freshness.
Pharmaceuticals
Ascorbic acid in pharmaceuticals boosts immune function, promotes collagen synthesis, enhances iron absorption, serves as an antioxidant, and treats vitamin C deficiency, offering extensive therapeutic benefits.
FAQ
What kinds of ascorbic acid are there to buy?
Ascorbic Acid is available in various forms including powder, tablets, capsules, and liquid formulations to suit different application needs.
Can Ascorbic Acid boost my immune system?
Yes, ascorbic acid plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system and may help reduce the severity and duration of colds.
How does the food sector use ascorbic acid?
Foods are preserved and have their flavor and color improved by the addition of ascorbic acid. Additionally, it helps keep food fresher for longer by avoiding rotting.
What distinguishes sodium ascorbate from ascorbic acid?
Ascorbic acid is the pure form of Vitamin C, while sodium ascorbate is a buffered form of Vitamin C, which is less acidic and may be easier on the stomach for some individuals.
What distinguishes L-ascorbic acid from D-ascorbic acid?
L-Ascorbic Acid is the biologically active form of Vitamin C found in nature, while D-Ascorbic Acid is a synthetic, less effective isomer.
